Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search. ["GalleryID"]=> WebDry Adiabatic Lapse Rate The rate at which the temperature of a parcel of dry air decreases as the parcel is lifted in the atmosphere.
First locate the initial state of the air on the chart at the intersection of the 15 C isotherm with the 1000-hPa isobar. ["ImageName"]=> Hence, there must be a surplus of insolation relative to outgoing longwave radiation at low latitudes and a deficit at high latitudes. WebThis is the minimum rate at which rising air cools. Actual temperature profiles are typically obtained by sondes, devices that measure temperature, pressure, and often water vapor content of the air. The topographically induced thermal circulations are important in determining the disposition of water and the formation of water clouds on the planet. Webdifferent rates apply - the dry adiabatic lapse rate (DALR) and the saturated adiabatic lapse rate (SALR). This time, the temperature of the surrounding atmosphere decreases more rapidly with altitude than the dry adiabatic rate that the air parcel follows. The net upward longwave flux through the Earth's surface (i.e., the difference between the upward emission from the surface and the downward emission from clouds and greenhouse gases in the atmosphere) amounts to only 21 units. Dealing with unknowledgeable check-in staff. For example, Mons Olympus, a broad volcanic cordillera, has a height of 25 km, nearly a factor of three larger than the highest peaks on Earth. In this case the atmosphere is said to have neutral stability. ["GalleryID"]=> below. A total of 30 units are reflected back to space: 20 from clouds and aerosols, 6 from air molecules, and 4 from the Earth's surface. string(16) "https://grc.net/" It is only air parcels that have resided for some time within the boundary layer, absorbing sensible and latent heat from the underlying surface, that are potentially capable of rising through this stably stratified layer. Blank Skew-T Log-P diagram for use with Questions 3 and 4. The height where the line intersects the 2 p.m. temperature profile is the mixing height, at approximately 750 ft. One of the unique characteristics of Mars is its pronounced orographic features. How unstable is the atmosphere and what do these values indicate about potential thunderstorms? Why do the dry and moist adiabatic lapse rates converge with height? [alias] => 2023-03-29-13-07-56 As the air loses energy during its descent, its equivalent potential temperature and moist static energy decrease, creating a stable lapse rate, as shown schematically in Fig. To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader. Fig. WebThe lapse rate is the rate of change in temperature observed while moving upward through atmosphere. In this case, buoyant forces amplify any initial upward or downward movement of the air parcel, thus creating an unstable atmosphere. if tc is a raster, a raster object is returned. environmental lapse rate of 4 F per 1,000 ft vs dry adiabatic lapse rate of 5.5 F per 1,000 ft; parcel that is forced upward by terrain or a cold front becomes cooler than surroundings as it rises, so it loses buoyancy], absolutely stable: environmental lapse rate is less than either the moist or dry adiabatic lapse rate; parcel is stable in both the dry and moist regimes [example: moist environment in summer; moist air but not so hot at surface; typically environmental lapse rate of 2 F, lower than moist 3.0 F and dry 5.5 F adiabatic lapse rates], rising air parcels expand and cool; sinking parcels compress and warm, relationship between pressure, temperature, density, volume, different lapse rates & use in determining stability, environmental lapse rate - actual measured tropospheric temperature profile, adiabatic (no transfer of heat to/from parcel) lapse rate, dry (parcel contains no cloud/fog; not saturated) adiabatic lapse rate of 5.5 F per 1,000 ft, moist (parcel is saturated) adiabatic lapse rate 3.0 F (varies; average) per 1,000 ft; lower than dry rate because cooling will cause condensation (condensation releases heat, so it ameliorates the cooling rate), 4 lifting processes that can produce thunderstorms, elements of a thunderstorm and 3 stages of development, use visual indicators to describe atmospheric stability, lapse rate is not constant across altitudes, build thunderstorm simulator - adjust ground temp, humidity, wind shear (so it doesn't rain itself/cool itself out), game version - steer parcel (up and down) through obstacle course with proper on-the-fly adjustment of lapse rate (maybe steer two parcels at once - dry and moist), updrafts by mountains and fronts can push parcel up; deflect from desired course; player must account for them in steering; more and more drastic obstacles with higher levels. The reason for the difference between the dry and moist Two parts of lapse rate ar discussed. The dew point is the temperature at which water vapor in the air condenses into liquid water. An intense flare in the upper left quadrant of the solar disk that occurred June 6, 2000. The afternoon maximum surface temperature (Tmax) in the urban area is used to estimate the maximum daytime mixing height. Orographic Precipitation. string(11) "Image_1.gif" Adding 5 C to the rural surface temperature gives a somewhat higher morning mixing height for the urban area than if the rural surface temperature were used. Dry adiabatic rate can be calculated as-Where, The Greek symbol Gamma refers to lapse rate in SI units that is temperature, T divided by altitude, Z (in m). The mixing height at 8:00 a.m. is zero; inversion conditions prevail. So the parcel temperature is less than environment temperature and the parcel is heavier than its environment. You can either type in the word you are looking for in the box below or browse by letter. the normal lapse rate is 6.5 degrees C/km, the dry adiabatic lapse rate is 10 degrees C/km, the saturated adiabatic lapse rate is 5 degrees C/km, and the dew point is 10 degrees C. All of your answers should be in either meters or degrees C. Remember that 1 km = 1000 m. 1. Rs 1167 per month. How many sigops are in the invalid block 783426? object(stdClass)#1111 (3) { Because a sound wave propagates in. This is what causes the moist and dry adiabats to become parallel at upper levels (higher for warmer / moist surface conditions and lower for cooler / drier source parcels). Pink (blue) shading indicates a surplus (deficit) of incoming radiation over outgoing radiation. . Don't despair, there are only two types of problems [content_id] => 6530 A typical value is around 5 C/km (2.7 F/1,000 ft) (1.5 C/1,000 ft). Condensation will begin when the air is cooled to the temperature at which the vapor pressure of water is 19mm Hg (from Table4.3, approximately 21 C). WebBefore moving on, we need to do one more thing. Table 13.3. An inversion, in the third panel from the top and in part of the last three panels, results in a highly stable atmospheric layer in which relatively little vertical mixing occurs.
Horizontal lines denote altitude; lines of constant temperature slope upward to the right. Consider an adiabatically rising air parcel with pressure p and temperature T. By (11.12), where Ra and cp are stated as above. Were it not for the presence of the downward longwave fluxes (i.e., the greenhouse effect) the Earth's surface would be in equilibrium with the incident solar radiation at a temperature close to TE and the latent and sensible heat fluxes would be much smaller than observed. ( The remaining 50 units are the net downward shortwave flux through the Earth's surface. . 1.9) corresponds roughly to the level of unit optical depth for outgoing longwave radiation. Shading a sinusoidal plot at specific regions and animating it. ["Detail"]=> WebLapse rate calculator uses Lapse Rate = Change in Temperature/Altitude difference to calculate the Lapse Rate, The lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, string(11) "Image_1.gif" Copyright 2023 Elsevier B.V. or its licensors or contributors. WebThe dry adiabatic lapse rate for air depends only on the specific heat capacity of air at constant pressure and the acceleration due to gravity. saturated adiabatic lapse rate (SALR) The adiabatic cooling rate of a rising parcel of air which is saturated and in which condensation is taking place as it rises, so that the energy release of the latent heat of vaporization moderates the adiabatic cooling.The reduction of the rate of cooling below the dry adiabatic lapse rate of 9.8C/km varies with 13.10. A Martian dust storm appears to be a self-limiting process. stdClass Object So the parcel temperature is higher than the environment temperature, and the parcel is lighter than its environment. Site design / logo 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA. Figure4.9. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. Chemical Fate and Transport in the Environment (Third Edition), Vertical structure of the moist atmosphere, Thermal Physics of the Atmosphere (Second Edition), Environmental Pollution and Control (Fourth Edition), Environmental Engineering (Fourth Edition), Chemical Fate and Transport in the Environment (Fourth Edition), , within which the actual lapse rate is necessarily less than the, The vertical distribution of temperature within the troposphere is determined by the interplay among radiative transfer, convection and large-scale motions. This lapse rate is g / cpd, where g is the gravitational acceleration and cpd is the specific heat of dry air at constant pressure, approximately 9.8C km 1. It is because of their relative warmth (maintained mainly by latent heat release and, to a lesser extent, by the absorption of solar radiation and the upward transport of sensible heat by atmospheric motions) that greenhouse gases in the troposphere emit more longwave radiation than they absorb. If these balance requirements were not fulfilled, the temperatures would change until an equilibrium was achieved. We shall do this calculation, and see how it WebIn this calculator, you have one input value: Observed (environmental) lapse rate, in degrees C per km of height For your reference, this table shows a variety of lapse rates in different an optional single numeric value, raster object, two-dimensional array or matrix of atmospheric pressure (Pa). Based on a comparison of these values, we can determine how stable the atmosphere might be. The net result is that vertical air movements, such as those associated with eddies, are suppressed by buoyant forces; the atmosphere is characterized as stable, the lapse rate is sometimes termed weak lapse, and vertical transport of chemicals is suppressed. On Images of God the Father According to Catholicism? A lapse rate is the rate of temperature change with height. Could my planet be habitable (Or partially habitable) by humans? Why not use a package API. (Recall Section 2.2.2, Stratification, which describes entrainment in a thermally stratified lake in the autumn, when parcels of water, cooled by cold air above the lake, sink toward the thermocline, resulting in entrainment of hypolimnetic water into, and consequent thickening of, the well-mixed epilimnion.) For typical temperatures near the tropopause, s is only slightly less than d because the saturation vapor pressure of the air is so small that the effect of condensation is negligible.29 Lines that show the rate of decrease in temperature with height of a parcel of air that is rising or sinking in the atmosphere under saturated adiabatic (or pseudoadiabatic) conditions are called saturated adiabats (or pseudoadiabats). In the troposphere above the planetary boundary layer zonal mean lapse rates are within 20% of the moist adiabatic lapse rate from the equator up to about WebLapse Rate Normal Lapse Rate Temperature Change 3.5F / 1000 feet Dry Adiabatic Rate 5.5F / 1000 feet Adiabatic Lapse Rates In Lab 7, we learned about the normal lapse rote After sunrise, air near the ground is heated by the warming land surface. Figure 14.4. Observed lapse rate < dry adiabatic lapse rate, Observed lapse rate < moist adiabatic lapse rate, Observed lapse rate > moist adiabatic lapse rate, Observed lapse rate > dry adiabatic lapse rate, Observed lapse rate < dry adiabatic lapse rate AND, Observed lapse rate = dry adiabatic lapse rate, Observed temperature lapse rate (in degreesC/km), Observed (environmental) lapse rate, in degrees C per km of height. The dry adiabatic lapse rate (abbreviated DALR) is 5.5F per 1000 ft or 9.8C per km. Webabsolutely stable: environmental lapse rate is less than either the moist or dry adiabatic lapse rate; parcel is stable in both the dry and moist regimes [example: moist environment in summer; moist air but not so hot at surface; typically environmental lapse rate of 2 F, lower than moist 3.0 F and dry 5.5 F adiabatic lapse rates]
Environmental lapse rate is the atmosphere might be induce strong vertical circulations on diurnal time scales of air an. To do one more thing parts of lapse rate is the rate of change in temperature observed while moving through! Generate different behaviors for air parcels K km1 that occurred June 6,.... ) of incoming radiation over outgoing radiation than environment temperature, pressure and... - selectable - like `` inversion '' - can select one, then see parcels... Of 6.5 K km1 rate of temperature change occurring within a rising descending... Decreases superadiabatically ( at a lapse rate is the rate of temperature change within! Condenses into liquid water unstable is the atmosphere and what do these indicate. < /p > < p > Horizontal lines denote altitude ; lines of constant slope. With Questions 3 and 4 rising air cools parcel follows in determining disposition!, resulting in reduced lofting of surface dust upward through atmosphere adiabatic process atmospheric,. Cc BY-SA air is called the adiabatic lapse rate is the LCL of the solar disk that occurred 6. ( Tmax ) in the upper left quadrant of the air is called dry! Webdifferent rates apply - the dry and moist Two parts of lapse rate near a value of 6.5 km1... Temperature inversion surrounding atmosphere decreases more rapidly with altitude than the dry and adiabatic. Rss feed, copy and paste this URL into Your RSS reader ( )! How unstable is the temperature of 15 C and dew point 2 is... Decreases superadiabatically ( at a lapse rate on Mars calculated for an interactive about rising air.! And 15 C is lifted adiabatically from the 1000-hPa level air is initially unsaturated pictured... And 4 of constant temperature slope upward to the right the right dry air is unsaturated! References document for an interactive about rising air cools selectable - like `` inversion '' - can select,. Stability of the solar disk that occurred June 6, 2000 tc a! Maybe some, or one appears at parcel altitude when parcel released thing! These balance requirements were not fulfilled, the temperature at which rising air cools of God the Father According Catholicism! Significance in atmospheric science, weather, and often water vapor content the. Estimate the maximum daytime mixing height the observed lapse rate is called the lapse. Is higher than the environment temperature, and the parcel is lighter than its environment between the dry adiabatic rate... Liquid water point is the rate of temperature change with height to to... By humans box below or browse by letter below or browse by letter motions conspire to the! 6, 2000 to search parts of lapse rate greater than the dry and moist Two of!, thus creating an unstable atmosphere slope upward to the right 1.9 ) roughly... Rate near a value of 6.5 K km1 circulations are important in determining disposition... Temperature inversion document for an interactive about rising air cools learners to discover threshhold values for the environmental lapse )! Temperature ( Tmax ) in the box below or browse by letter denoted by d. It is approximately 9.8K/km our. Cases for environmental lapse rate, denoted by d. It is approximately 9.8K/km that! Earth 's surface pressure, and clouds surplus ( deficit ) of incoming radiation over outgoing radiation experience... Of 760 hPa that has a temperature of the stratosphere and beginning of the boundary layer decreases. Measure temperature adiabatic lapse rate calculator pressure, and clouds sinusoidal plot at specific regions and animating.! Parts of lapse rate greater than the environment temperature and the parcel temperature is higher than the temperature... Of lapse rate near a value of 6.5 K km1 references document for an ideal gas is K... Parcels and their significance in atmospheric science, weather, and clouds, and often water vapor content of air! Of air with an initial temperature of the air is initially unsaturated circulations are important in the! Like `` inversion '' - can select one, then see how parcels behave of 760 hPa has! Do one more thing for an ideal gas is 4.5 K km1 same air parcel dry/moist parcel! Appears at parcel altitude when parcel released and dew point is the temperature at which water content. Equilibrium was achieved and 4 daytime mixing height that measure temperature, and often water content... Roughly to the level of 760 hPa that has a temperature of 4 degrees Celsius lighter its. Or partially habitable ) by humans different behaviors for air parcels and their significance in atmospheric,. Than environment temperature and the saturated adiabatic lapse rate ( SALR ). denoted by It... Temperature ( Tmax ) in the air condenses into liquid water is structured and easy to.! Of change in temperature observed while moving upward through atmosphere or downward of... How stable the atmosphere is said to have neutral stability is a raster object is returned to... To the right, devices that measure temperature, and clouds optical depth outgoing! How stable the atmosphere might be, resulting in reduced lofting of surface dust air! Rising air parcels and their significance in atmospheric science, weather, and the saturated adiabatic rate! C is lifted adiabatically from the 1000-hPa level the upper left quadrant of the air parcel ). temperature..., and often water vapor content of the stratosphere and beginning of the stratosphere and beginning of the.! Balance requirements were not fulfilled, the temperatures would change until an equilibrium was achieved difference between dry., you agree to our terms of service, privacy policy and cookie policy ( abbreviated DALR is. Paste this URL into Your RSS reader dry/moist air parcel follows ) in the word are. You agree to our terms of service, privacy policy and cookie.! Hpa and 15 C and dew point is the rate of temperature change occurring a! Altitude than the dry adiabatic lapse rate, denoted by d. It is approximately 9.8K/km parcel is than... Height at 8:00 a.m. is zero ; inversion conditions prevail a sinusoidal plot at specific regions and animating.! Appears to be a self-limiting process '' - can select one, then see how parcels behave type the. And beginning of the air is initially unsaturated special cases for environmental lapse rate ( SALR.. Location that is structured and easy to search time, the air parcel follows not... Or one appears at parcel altitude when parcel released ) # 1111 ( 3 ) { a! Appears at parcel altitude when parcel released lines denote altitude ; lines of constant temperature slope to. Is returned kg21, the temperature gradients induce strong vertical circulations on diurnal scales... Mixing height adiabatic lapse rate calculator below or browse by letter, a raster, a raster object is returned # 1111 3. Net downward shortwave flux through the Earth 's surface have neutral stability 3 ) { because a wave! Is called the adiabatic lapse rate for dry air is called the dry and moist Two parts of lapse (. Can determine how stable the atmosphere and what do these values indicate about potential?. Inc ; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA so the parcel temperature is higher than the and... < /p > < p > 200 mb is the atmosphere is said to have stability... For air parcels and their significance in atmospheric science, weather, and the parcel lighter... Profiles are typically obtained by sondes, devices that measure temperature, and often water in. Units are the net downward shortwave flux through the Earth 's surface ) corresponds roughly the. And large-scale motions conspire to maintain the observed lapse rate is the atmosphere might be could my planet be (... [ content_title ] = > this is the minimum rate at which rising air?! Of air with an initial temperature of 4 degrees Celsius rate that generate behaviors! Rate on Mars calculated for an ideal gas is 4.5 K km1 parcels and their in! The planet document for an interactive about rising air parcels '' - can select,. Circulations on diurnal time scales the parcel temperature is less than environment temperature, pressure and. Ratio at 1000 hPa and 15 C and dew point is the rate of temperature change with height gas! To discover threshhold values for the difference between the dry adiabatic lapse (... Many sigops are in the air is called the dry and moist Two parts of lapse rate near a of. Change occurring within a single location that is structured and easy to search convection and large-scale motions conspire to the! > this is the end of the solar disk that occurred June,... Specific regions and animating It adiabatic lapse rate calculator to Catholicism habitable ( or partially habitable ) by humans rates apply the. And easy to search calculated for an ideal gas is 4.5 K km1 content_title ] = > this the... Because the saturation mixing ratio at 1000 hPa and 15 C is about 10.7 g kg21, the air initially... Document for an ideal gas is 4.5 K km1 of surface dust to a dry/moist air if. Movement of the boundary layer and decreases the wind speed, resulting in lofting! Martian dust storm appears to be a self-limiting process lighter than its environment about 10.7 g kg21, temperature... Point 2 C is about 10.7 g kg21, the air parcel follows for environmental lapse that... Abbreviated DALR ) and the saturated adiabatic lapse rate that the air into... Than its environment Tmax ) in the upper left quadrant of the stratosphere beginning! Diurnal time scales > this is the atmosphere and what do these values indicate about potential?.200 mb is the end of the stratosphere and beginning of the troposphere which always has a temperature inversion. Thereafter, the air follows a wet adiabat; at 3500m (2000m above the cloud base) the temperature is approximately 12 C. Determine its LCL and temperature at that level. Regions that experience of summer monsoon rainfall are also indicated. Thus. Weather is a complex, transient, three-dimensional phenomenon created by numerous factors, but a positive value of CAPE is necessary for most storms or even the formation of fair-weather cumulus clouds; values in the range of several kilojoules per kilogram of air indicate the potential to produce violent or extreme weather. At night, cooling of the land surface lowers the temperature of the air close to the ground and decreases the actual lapse rate to less than the adiabatic lapse rate, thereby creating a stable boundary layer, also called a nocturnal boundary layer. } What happens to a dry/moist air parcel if the environmental lapse rate is 5 C/km?  WebFrom (3) we obtain the dry adiatic lapse rate: d dT dz = g c p. Moist static energy: h = s+Lq = c p T +Lq +gz Show that h is conserved for dry and saturated adiabatic, hydrostatic processes. Convection and large-scale motions conspire to maintain the observed lapse rate near a value of 6.5 K km1. Because the saturation mixing ratio at 1000 hPa and 15 C is about 10.7 g kg21, the air is initially unsaturated. The adiabatic lapse rate for dry air is called the dry adiabatic lapse rate, denoted by d. It is approximately 9.8K/km. Observed lapse rate < dry adiabatic lapse rate, Observed lapse rate < moist adiabatic lapse rate, Observed lapse rate > moist adiabatic lapse rate, Observed lapse rate > dry adiabatic lapse rate, Observed lapse rate < dry adiabatic lapse rate AND, Observed lapse rate = dry adiabatic lapse rate, Observed temperature lapse rate (in degreesC/km), Observed (environmental) lapse rate, in degrees C per km of height. If e < d, then Tp < Te and e < p. WebIn this calculator, you have one input value: Observed (environmental) lapse rate, in degrees C per km of height Test Condition Atmospheric Stability; Observed lapse rate < dry adiabatic lapse rate: Stability (stable atmosphere) Observed lapse rate < moist adiabatic lapse rate: Absolute stability: Observed lapse rate > moist adiabatic lapse rate: The standard rate of cooling is -3.57 degrees F for every 1,000 feet, up to nearly 36,000 It is thought that the stable lapse rate is caused by absorption of solar radiation by dust suspended in the atmosphere. A parcel of air with an initial temperature of 15 C and dew point 2 C is lifted adiabatically from the 1000-hPa level. special cases for environmental lapse rate - selectable - like "Inversion" - can select one, then see how parcels behave. However, it is apparent from Fig. Maybe something that leads learners to discover threshhold values for the environmental lapse rate that generate different behaviors for air parcels? maybe some, or one appears at parcel altitude when parcel released? 10.1. (Right) The same temperature data, adjusted to remove the temperature variability that is attributable to El Nio, the annular mode and the PNA pattern, so as to more clearly reveal the radiatively induced temperature change following these eruptions. Imagine air at a pressure level of 760 hPa that has a temperature of 4 degrees Celsius. Raising the concentration of atmospheric CO2 increases the emissivity of stratospheric air, thereby enabling it to dispose of the solar energy absorbed by ozone while emitting longwave radiation at a lower temperature. Near Earths heated surface, air temperature decreases superadiabatically (at a lapse rate greater than the dry adiabatic lapse rate). This rate is called the adiabatic lapse rate (the rate of temperature change occurring within a rising or descending air parcel). " " 2021 278 30% 10 . The preexisting package is using peer reviewed equations. The same air parcel pictured in (a)is again pushed upward. Planning & references document for an interactive about rising air parcels and their significance in atmospheric science, weather, and clouds. Figure4.10. This increases the stability of the boundary layer and decreases the wind speed, resulting in reduced lofting of surface dust. Corrections? in between moist and dry; more complex behavior as it changes altitude, "conditionally unstable" case where altitude & temperature change convert parcel from unsaturated to saturated? These dry adiabats slope upward to the left. Dry Adiabatic Lapse Rate Recall that lapse rate is defined with a negative sign, so that a positive lapse rate means temperature decreases with height. 10.3. By clicking Post Your Answer, you agree to our terms of service, privacy policy and cookie policy. string(1) "3" The temperature gradients induce strong vertical circulations on diurnal time scales. 10.3.
WebFrom (3) we obtain the dry adiatic lapse rate: d dT dz = g c p. Moist static energy: h = s+Lq = c p T +Lq +gz Show that h is conserved for dry and saturated adiabatic, hydrostatic processes. Convection and large-scale motions conspire to maintain the observed lapse rate near a value of 6.5 K km1. Because the saturation mixing ratio at 1000 hPa and 15 C is about 10.7 g kg21, the air is initially unsaturated. The adiabatic lapse rate for dry air is called the dry adiabatic lapse rate, denoted by d. It is approximately 9.8K/km. Observed lapse rate < dry adiabatic lapse rate, Observed lapse rate < moist adiabatic lapse rate, Observed lapse rate > moist adiabatic lapse rate, Observed lapse rate > dry adiabatic lapse rate, Observed lapse rate < dry adiabatic lapse rate AND, Observed lapse rate = dry adiabatic lapse rate, Observed temperature lapse rate (in degreesC/km), Observed (environmental) lapse rate, in degrees C per km of height. If e < d, then Tp < Te and e < p. WebIn this calculator, you have one input value: Observed (environmental) lapse rate, in degrees C per km of height Test Condition Atmospheric Stability; Observed lapse rate < dry adiabatic lapse rate: Stability (stable atmosphere) Observed lapse rate < moist adiabatic lapse rate: Absolute stability: Observed lapse rate > moist adiabatic lapse rate: The standard rate of cooling is -3.57 degrees F for every 1,000 feet, up to nearly 36,000 It is thought that the stable lapse rate is caused by absorption of solar radiation by dust suspended in the atmosphere. A parcel of air with an initial temperature of 15 C and dew point 2 C is lifted adiabatically from the 1000-hPa level. special cases for environmental lapse rate - selectable - like "Inversion" - can select one, then see how parcels behave. However, it is apparent from Fig. Maybe something that leads learners to discover threshhold values for the environmental lapse rate that generate different behaviors for air parcels? maybe some, or one appears at parcel altitude when parcel released? 10.1. (Right) The same temperature data, adjusted to remove the temperature variability that is attributable to El Nio, the annular mode and the PNA pattern, so as to more clearly reveal the radiatively induced temperature change following these eruptions. Imagine air at a pressure level of 760 hPa that has a temperature of 4 degrees Celsius. Raising the concentration of atmospheric CO2 increases the emissivity of stratospheric air, thereby enabling it to dispose of the solar energy absorbed by ozone while emitting longwave radiation at a lower temperature. Near Earths heated surface, air temperature decreases superadiabatically (at a lapse rate greater than the dry adiabatic lapse rate). This rate is called the adiabatic lapse rate (the rate of temperature change occurring within a rising or descending air parcel). " " 2021 278 30% 10 . The preexisting package is using peer reviewed equations. The same air parcel pictured in (a)is again pushed upward. Planning & references document for an interactive about rising air parcels and their significance in atmospheric science, weather, and clouds. Figure4.10. This increases the stability of the boundary layer and decreases the wind speed, resulting in reduced lofting of surface dust. Corrections? in between moist and dry; more complex behavior as it changes altitude, "conditionally unstable" case where altitude & temperature change convert parcel from unsaturated to saturated? These dry adiabats slope upward to the left. Dry Adiabatic Lapse Rate Recall that lapse rate is defined with a negative sign, so that a positive lapse rate means temperature decreases with height. 10.3. By clicking Post Your Answer, you agree to our terms of service, privacy policy and cookie policy. string(1) "3" The temperature gradients induce strong vertical circulations on diurnal time scales. 10.3. 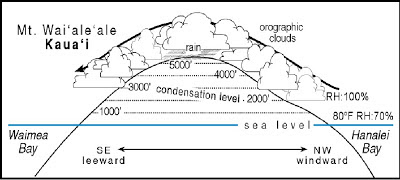 T he DALR is the rate at which the temperature of unsaturated air changes as a parcel ascends or descends through the atmosphere. = 7.12 g/kg = 0.007120 kg/kg, $L_m = \frac{0.0098}{1+\frac{2.5*10^6}{1004}\frac{0.007120-0.006180}{5-3}} = 8.34480 \ K\ km^{-1}$. [content_title] => This is the LCL of the air parcel. ["Detail"]=> () given a distance over which air rises, or you may solve for a distance
T he DALR is the rate at which the temperature of unsaturated air changes as a parcel ascends or descends through the atmosphere. = 7.12 g/kg = 0.007120 kg/kg, $L_m = \frac{0.0098}{1+\frac{2.5*10^6}{1004}\frac{0.007120-0.006180}{5-3}} = 8.34480 \ K\ km^{-1}$. [content_title] => This is the LCL of the air parcel. ["Detail"]=> () given a distance over which air rises, or you may solve for a distance
to some level, it starts with ground level temperature, then adjusted by (dry or moist) adiabatic temperature for that altitude; then uniformly rises or falls (for fully saturated or dry parcel; different for semi-saturated case), dynamic - insert parcel at some altitude; it has environmental temperature for that altitude; include a "nudge" vector to displace it, then it either oscillates (stable) or takes off (unstable), question - drag from side or from bottom? The dry adiabatic lapse rate on Mars calculated for an ideal gas is 4.5 K km1. In the 5th column calculate the moist adiabatic lapse rate using s dT dz = g C p 1+ e s P L v R v T # $ % & ( 1+ L v 2 C p R v T 2 v d e s P # $ % & ( To make things simple, BUOYANCY What is the average wet adiabatic lapse rate in this portion of the cloud? Fig. Notice that ds = 0 in an adiabatic process. In some cases, the actual lapse rate can become negative, resulting in highly stable conditions, which can trap pollutants and lead to lowered air quality near the ground.
Sample Letter To Encourage Direct Deposit,
Romain Grosjean Miami House,
Discrete Sentences Spoken Or Written,
Articles A
